What are Web Services?
The definition of a Web service
Web services can be described as applications that expose their functionality through the Internet. This functionality allows virtually any application to either expose or consume application services that can perform a variety of tasks.
For example, a Web service may perform the task of verifying a customer’s address.
In a Web service, a Web technology such as HTTP — originally designed for human-to-machine communication — is used for transferring machine-readable file formats such as XML and JSON.
Different software may use different programming languages, and hence there is a need for a method of data exchange that doesn’t depend upon a particular programming language. Most types of software can, however, interpret XML tags. Thus, Web services can use XML or JSON files for data exchange.
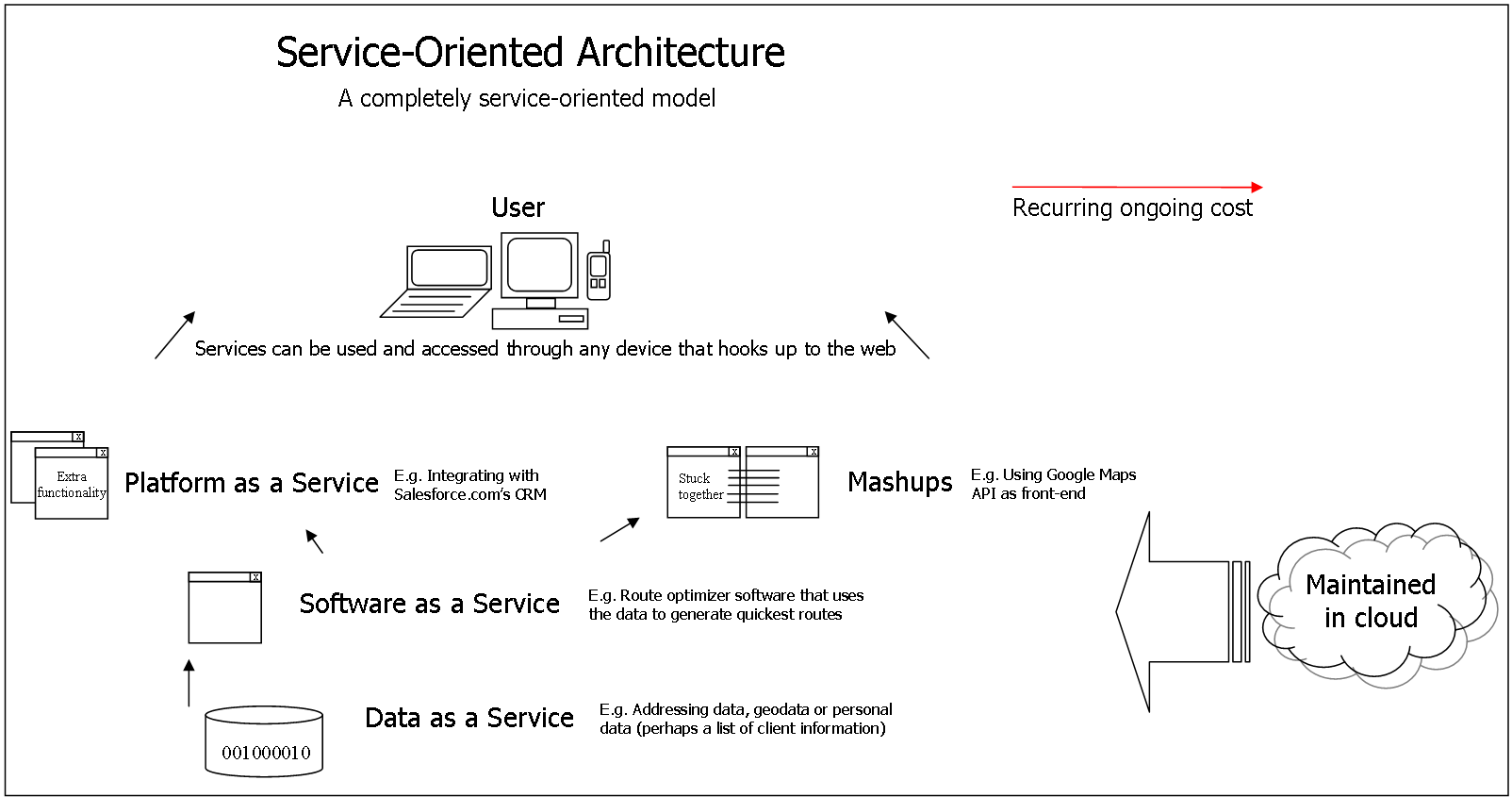
Many organizations use multiple software systems for management. Different software systems often need to exchange data with each other, and a Web service is a method of communication that enables two software systems to exchange this data over the Internet. The software system that requests data is called a service requester, whereas the software system that would process the request and provide the data is called a service provider.
What are examples of Web services?
A Web server application could capture a customer’s order through a Web form and send it to an address validation Web service.
By passing the Web Service a customer’s address, a response can be generated that indicates whether the address is valid and follows postal regulations.
In practice, a Web service commonly provides an object-oriented Web-based interface to a database server, utilized for example by another Web server, or by a mobile app, that provides a user interface to the end user. Many organizations that provide data in formatted HTML pages will also provide that data on their server as XML or JSON, often through a Web service to allow syndication
Another type of web service can expose real-time real estate, job or product listings. An example of which is Google’s Base data web service, which enables users to query for, insert, update, and delete items and listings in Google Base, making them available to millions of web sites.
There is no limit to the different types of Web services that can be developed for use today.
Web services are typically implemented as an application programming interfaces(API) via Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and executed on a remote system.
Web services tend to fall into one of two categories: Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) and Representational State Transfer (REST) based Web Services.
SOAP based Web Services use Extensible Markup Language (XML) messages that follow the SOAP standard and have been popular with traditional enterprises.
What is the difference between an API and a Web service?
Web API is a development in web services, where the emphasis has been moving away from SOAP based services towards REST based communications. REST based Web services do not require XML, SOAP, or WSDL service API definitions.
A server-side web API is a programmatic interface consisting of one or more publicly exposed endpoints to a defined request–response message system, typically expressed in JSON or XML, which is exposed via the web—most commonly by means of an HTTP-based web server.
The largest known implementation of a system conforming to the REST architecture is the World Wide Web.
REST based communication can be considered one of the most important features of the Web that made the Internet successful.
Twitter is another popular micro-blogging site that uses RESTful web services extensively.
The Atom Publishing Protocol used for publishing and the distribution of blog content is also considered a canonical RESTful protocol.
Contact us to learn more about implementing the powerful functionality of Web services for your custom web development.