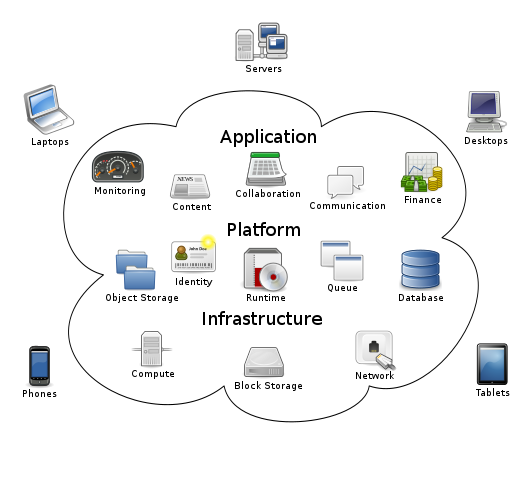
Cloud software development enables companies to avoid or minimize information technology infrastructure costs.
Cloud software development enables businesses to get their applications up and running faster, with improved manageability and less maintenance, and it enables businesses to more rapidly adjust resources to meet fluctuating and unpredictable demand, providing burst computing capability: high computing power at certain periods of peak demand.
Cloud based vs. On-premises software
Cloud-based software is usually served via the internet and it can be accessed by users online regardless of the time and their location. Unlike on-premises software, cloud-based software users only need to install an application or a web browser in order to access its services.
On-premises software is installed and runs on computers on the premises of the organization using the software, rather than at a remote facility such as a the cloud.
On-premises software is established within the organization’s internal system along with the hardware and other infrastructure necessary for the software to function.
On-premises software drawbacks:
- Compatibility with hardware, other software, and operating systems.
- Licensing cost and restrictions.
- Maintenance, support, and patch revision processes.
For small and medium-sized businesses looking for ways to control cost, modernize systems, and consume on-demand solutions, software licensing has become a very expensive and complicated issue.
This affects strategy, economics, and eventually technical decisions on how to move forward in the face of broken budgets and Return on Investment (ROI) calculations
With on-premises software, there are several costs expected to incur until the software and its services would be fully available for use. First, the installation of on-premises software within the organization requires high initial costs including costs incurred for the purchase of hardware and other infrastructures. In addition to this, the entity is subjected to the purchase of the license particular to the software which involves costs and time for the preparation. In order to maintain the software functionality, sustainable maintenance and operations are required and the entity will be subjected to the costs incurred for these as well.
For cloud-based software, in general, the initial costs required for the use of software services are considered relatively low and thus suitable to small enterprises without a large amount of capital. Moreover, cloud-based software users are not subjected to license fees as well as maintenance and operation costs because these are handled by software vendors. Additionally, costs incurred for infrastructures are smaller compared to on-premises software as users only need their electronic devices to be able to get access to the services.
Operation and maintenance
The entity using on-premises software are fully responsible for the daily operation, maintenance and security of the system by itself. This results in more time and costs required for the system operation as well as IT personnel who have specialization in managing the system.
For cloud-based software, it’s the software provider who is responsible for the system operations and maintenance. So, no IT professionals need to be hired within the entity specifically for the purpose of operating the software.
Backup and data storage
As for the maintenance and operations, the entity using on-premises software is also responsible for backup and storage of software data.
For cloud-based software, the entity has no requirement of data backup by itself, as this is also a responsibility of the cloud software provider and data backup is included.
Custom Software
Historically the user/subscriber of cloud software did not have access to the underlying infrastructure, application code, or individual application attributes except for a set of named user-specific application configuration settings.
Although on-premises software previously had the huge advantage of being capable of customization and tailoring software services to each business needs, Nexus Software Systems’ cloud based software has evolved as a platform where customizable cloud services are now available.
Custom cloud software development is able to be delivered at a lower cost and have universal access. These new models center around new licensing models tied to multiple users, a certain level of access, and service-level agreements (SLA) rather than the size of the software infrastructure deployment.
With software as a service (SaaS), the subscriber uses the provider’s centralized application deployed using cloud infrastructure. SaaS enables access from any approved client device, browser, or custom interface.
With custom cloud based software development, organizations have potentially limitless possibilities for running applications that may not have been otherwise possible given the limitations of their corporate systems, infrastructure, or resources. If the right middleware and associated components are deployed, cloud based software can present massive incentives and benefits. Organizations can quickly realize benefits from scalability, flexibility, and on-demand self-service capabilities.
Customer adoption increases as access to data and applications can be from virtually anywhere, at any time with internet access. Additional benefits include: Cost control, cost reduction Licensing or support becomes a built-in component for the provider and the subscriber benefits from economies of scale.
The purchasing of up-front bulk licensing and the associated capital expenditure is removed and replaced by demand-based pay-as-you-go licensing models.
User-based internal support requirements reduce significantly as the software cloud service provider can typically handle more of the support at scale.
Cloud Software Development
- Ease of use
- Automatic updates and patch management
- Improved security
- Standardization and compatibility
- Global accessibility
Software-as-a-Service provides a fully managed application. The consuming organization manages the user base, access to the service, and the governance of the data inputted by organizational users. The Cloud Service Provider has full responsibility for the architecture, security, and availability of the service.
Some of the most popular SaaS service offering categories are as follows:
- CRM software: Customer information management, marketing automation, and sales pipeline tracking.
- ERP software: Improved process efficiency and organizational information sharing combined with improved management insight into workflow and productivity.
- Accounting software: Improved financial organization and tracking.
- Project management software: Project/program scope, requirements, and progress management. The tracking of changes, communications, and deadlines in a way that meets stakeholder requirements.
- Email marketing software: Automate email marketing and relationship building, while optimizing message delivery.
- Billing and invoicing software: Billing and invoicing automation. Implementing customer self-service payment options. The reduction of data entry costs, and elimination of billing errors.
- Collaboration software: Improved organizational communications that empower employees to more easily follow complex interactions. More efficient communications and enhanced enterprise productivity.
- Web hosting and e-commerce: Web hosting, content management systems, message boards, shopping carts, and so on.
- HR software: Employee time tracking. Improved recruiting and hiring. Automate payroll and more efficient management of human resources.
- Transaction processing: Credit cards and bank transfer processing.
The cloud (or SaaS) model has no physical need for indirect distribution because it is not distributed physically and is deployed almost instantaneously, thereby negating the need for traditional partners and middlemen. Unlike traditional software, which is conventionally sold as a perpetual license with an up-front cost (and an optional ongoing support fee), SaaS providers generally price applications using a subscription fee, most commonly a monthly fee or an annual fee. Consequently, the initial setup cost for SaaS is typically lower than the equivalent on-premises software. SaaS vendors typically price their applications based on some usage parameters, such as the number of users using the application.
A key driver of SaaS growth is SaaS vendors’ ability to provide a price that is competitive with on-premises software. This is consistent with the traditional rationale for outsourcing IT systems, which involves applying economies of scale to application operation, i.e., an outside service provider may be able to offer better, cheaper, more reliable applications.
Cloud computing is a way to access information and applications online instead of having to build, manage, and maintain them on your own hard drive or servers. It’s fast, efficient, and secure.
The advantages of cloud computing for your business
Now that you understand how it works, it’s easy to see that cloud computing has many advantages. Among the most important benefits of cloud computing, for example, are:
Convenience
Cloud computing makes storing, retrieving, and sharing information fast and easy.
Flexibility
Because information flows across locations and devices, employees can work safely and securely from anywhere. That makes them more productive, collaborative, and satisfied in their jobs.
Cost
Maintaining on-premise infrastructure is time-consuming and costly, with security patches and operating system updates.
Cloud computing storage enables you to host applications on remote servers, saving you the headache of hardware-related costs.
You can scale up your business depending on your needs without incurring the costs of managing your servers. You don’t need to hire a large team to maintain your cloud infrastructure to keep everything running smoothly.
Accounting
Cloud computing is beneficial from an accounting standpoint because it allows IT infrastructure to be classified as an operational instead of capital expenditure. That’s usually better for business health because operational expenses are tax-advantaged and pay-as-you-go. That translates to more flexibility, less waste, and often better ROI.
Reliability
Cloud service providers continually refine their architecture to deliver the highest standards of performance and availability. Meanwhile, the third parties that host their services constantly maintain and update them, and provide easy access to customer support. This commitment to continuous improvement makes them dependable in standards of excellence.
Scalability
Cloud vendors generally allow customers to increase or decrease computing resources as needed. That means cloud computing can scale up or down with your business. You can add or subtract bandwidth, users, and services, and even add more service providers. In addition, many cloud service providers will automate this scaling on your behalf so teams can dedicate more time to customer experience and less time to capacity planning.
As a business, the ability to react quickly is key. The cloud can help you achieve that by offering speed, flexibility and scalability. It also makes it easier to get your application deployed without having to purchase expensive hardware or software upfront.
The Cost of Speed
What’s the cost of not being fast? The answer is simple: you lose customers. Today, speed is more important than ever before. Speed of development, deployment and scaling all play a role in keeping your customers happy. But there’s another aspect to speed that many companies overlook: innovation. If you want to innovate, you have to be able to move quickly—and that requires agility from your technology partners as well as from within your own company.
Cross Platform Solutions
With cloud software development, you can access your solution from any device. That includes:
- Laptops
- Tablets
- Smartphones
All of these are a part of what is known as the “mobile workforce.” The mobile workforce refers to people who work anywhere and everywhere, using whatever device they have on them at that moment. Cloud software development allows all users to access the same files and data seamlessly across all devices. Not only that, but it also offers easy collaboration between employees no matter where they are located!
Security is Paramount
Security is a cornerstone of cloud software development. Cloud software development companies have secure cloud networks and data centers that are protected by firewalls. They also offer encryption systems to ensure your information is secure when it’s being transmitted or stored.
Cloud software development companies are more likely than others to use the most advanced security measures, since they know how important it is for businesses today. The best thing you can do as an IT manager or developer is work with a company that knows its stuff when it comes to security (and other areas of technology).
These benefits will surely give you a competitive advantage.
At the end of the day, you have to choose what’s best for your company. But if you take into account all of the benefits that cloud software development offers, such as cost savings and increased security, it seems like there are many reasons why businesses should choose this route. And with these benefits giving you a competitive advantage over others in your industry, it’s hard to see how on-premises solutions could ever beat out cloud ones.
Conclusion
Custom Cloud software development is the future of business, and it’s here to stay. If you want to get a head start on your competitors and start reaping the benefits of cloud software development today, then contact us today.
References: